Retina Laser Surgery
Photocoagulators are especially well suited for delicate retinal work. In the case of a retinal tear or hole, the scar tissue helps hold the retina in place. Photocoagulation can seal up leaking vessels, as in the case of proliferative diabetic retinopathy, or destroy diseased retinal tissue. Photocoagulation can also be used for choroidal neovascularization.
Retinal Care Portfolio
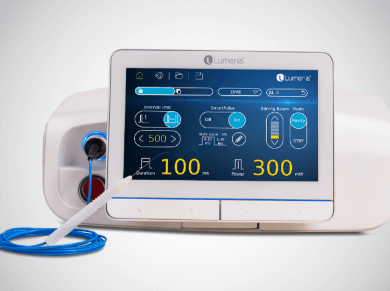
Smart532™
Green Photocoagulator with SmartPulse™ Sub-Threshold Technology
Array™ LaserLink™
Pattern Scanning
Laser Technology
Smart Selecta Trio
SLT + YAG + Smart532™
Your Smart Comprehensive Solution
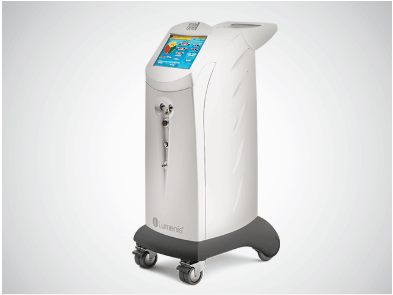
Vision One
Multi-Wavelength Photocoagulator
Green 532nm, Yellow 577nm and Red 659nm
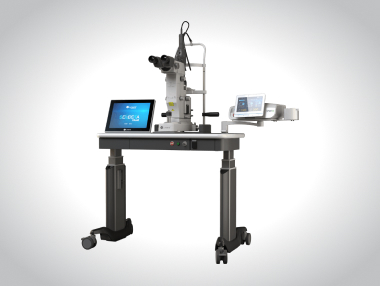
Novus Spectra
Green Dual-Port Photocoagulator for the OR and Clinic
LIOs
Advanced Laser Indirect Ophthalmoscopes
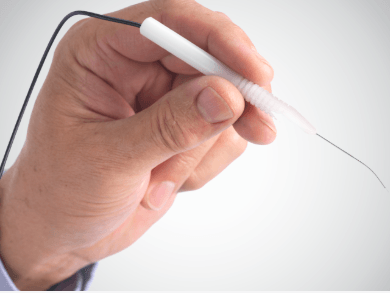
LumeProbe™
Endo-Photocoagulation Laser Probes
Retinal Indications Overview
Photocoagulators cauterize blood vessels with heat generated by the laser beam. The laser creates tiny, controlled burns that create adhesive forming scar tissue. The Lumenis line of photocoagulators and delivery devices are designed to give ophthalmologists the breadth and depth they need to treat several types of conditions including:
Meeting the Challenge of Retinal Surgery
Lumenis’ line of gold-standard photocoagulators is created for the delicate demands of sophisticated retinal surgery.
While diseases of the retina are plentiful, the retina generally responds well to laser treatment. As clinical capabilities within ophthalmology increase, so do your options in selecting a laser. The Lumenis family of retinal lasers offer treatment versatility and optimize therapeutic effect, for today’s most challenging retinal procedures.
Key Indications:
PB-2006798 Rev A